Information
General commercial and delivery term
I. GENERAL PROVISIONS
-
These General Commercial and Delivery Terms apply to the full extent unless the seller and the buyer agree some conditions otherwise in a purchase contract.
-
No alterations, amendments and supplements to these Terms and to a purchase contract shall be effective unless made by means of a written agreement of both contracting parties.
-
Any agreements, whether oral or written, made prior to the completion of a purchase contract by both parties shall become null and void unless included in the purchase contract or unless in compliance with these General Terms.
-
Offers are only binding if this is indicated in writing therein.
II. DELIVERY OF GOODS
-
The delivery of goods is effected under a purchase contract concluded between the buyer and the seller, or under a purchase order placed by the buyer and a written confirmation of the purchase order by the seller, which constitutes the conclusion of a purchase contract.
-
The term of delivery of goods is indicated by the date given in the purchase contract. Should the seller anticipate that a delay of delivery might occur, the seller shall inform the buyer of the change.
-
In the event of such occurrence that cannot be anticipated at the time when the purchase contract is signed and that will form a bar to the performance of contractual obligations by the seller, the seller is entitled to postpone the term of performance by the time of existence of such occurrence and by a reasonable time necessary to start up its normal operation.
-
The seller has the right to fail to observe the agreed terms of delivery due to the following causes:
a/ act of God
b/ breakdown of technological equipment
c/ administrative measures
d/ shortage of power or basic materials -
Should the above mentioned causes persist for more than one month from the date of the agreed term of delivery, both the seller and the buyer have the right to withdraw from the contract without claims for compensation.
-
Transport of goods is carried out upon an agreement of the seller and the buyer stipulated in the purchase contract. The delivery of goods is subject to the provisions of INCOTERMS 2000.
III. TERMS OF PAYMENT
-
The terms of payment are stipulated in the purchase contract.
-
A payment is considered to be effected when the due amount as per invoice is credited in full to the bank account of the seller. The buyer will be in default of payment of an invoice if the due date mentioned in the invoice is not observed.
-
If the buyer is in default of payment the seller is entitled to retain deliveries not yet performed under all purchase contracts concluded with the buyer. This, however, will not constitute a breach of contract or a right to withdraw from the contract.
-
If the buyer is in default of payment of an invoice, the seller is entitled to charge the buyer with an interest on late payment amounting to 0.05% of the amount outstanding for each day of the delay, starting from the due date of the outstanding amount to the day when this amount is credited to the bank account of the seller.
IV. RIGHT OF OWNERSHIP TO THE GOODS
-
The buyer acquires the right of ownership by paying the purchase price in full. The seller and the buyer can agree in writing other date of acquisition of title, or the way of disposal of the goods before the passage of ownership onto the buyer.
V. COMPLAINTS
-
The buyer is obliged to inspect the goods during acceptance.
-
The claims of the buyer in the event of delivery of defective goods will lapse unless presented in writing within 14 days from the date of delivery to the seller.
-
When making a complaint, the buyer shall mention all the necessary details of the defect. The seller has a right to inspect the goods about which the complaint is made or to have the goods inspected by an authorized person.
-
The seller can, at its option, either replace the defective goods, or repair them, and/or have them repaired, or give an adequate discount.
-
Natural differences in colour and structure do not constitute grounds for complaint. The applicable PN and EN standards are of crucial importance when considering justification of a claim.
-
Differences in quantity within + or - 5% do not constitute grounds for complaint.
VI. FINAL PROVISIONS
-
The goods are manufactured in accordance with valid PN and EN standards.
-
Liability of the seller is governed by these "General Terms" only. Any claims, including claims for damages are precluded unless stated in these "General Terms".
-
The place of business of the seller is the place of performance of deliveries under a contract.
-
Any disputes that might arise between the parties in connection with the performance of contractual obligations shall be resolved in an amicable way. If, however, a dispute cannot be settled by an agreement, it is agreed that such dispute shall be submitted to the court of law having jurisdiction according to the place of business of the seller.
Storage and freight
We will provide you with advice regarding transport and preservation of our products.
The inevitable properties of plywood materials include shrinkage, width or length swelling and winding, which are due to the nature of wood material. Some defects may be avoided by careful processing, yet many of such discrepancies are due to ill storage or improper processing practices as not all the consumers may be aware of plywood characteristics.
Incorrect handling in storage and further processing result in twisting and winding.
Plywood materials may not be stored in open-space areas, not even under open sheds (except for the foil lined pieces). These materials shall be stored in dry, closed and dust free premises without any significant deviations in temperature or relative humidity.
Besides the above conditions, these materials may not be stored in the close vicinity of heating units (space heaters, etc.).
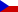
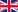
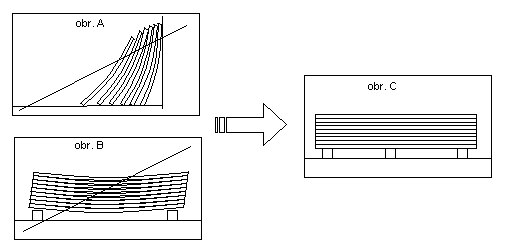
It is recommended not to set these sheets on the edge or to lean them against walls (see Fig. A). These materials must always be stored is stacks laid horizontally on dry and level bearers. These bearers shall be identical in thickness and laid in order to prevent any creeping (see Fig. B,C). It is not recommended to process any plywood materials immediately after delivery. These should be rather kept at the workshop for a certain period to attain the humidity level of processing environment.
Plywood materials can be transported by train or road haulage, whereas the load shall be fixed properly and secured (e.g. with tarpaulin) to ensure protection from direct effect of weather conditions.
Terminology
| Term | Definition |
| Plywood | Wood-based panel consisting of an assembly of layers glued together with the direction of the grain in adjacent layers usually at right angles. |
| Balanced plywood | Plywood in which the layers are symmetrical about the central layer with respect to thickness, grain orientations and species. |
| Veneer plywood | Plywood in which all the layers are made of veneers oriented parallel to the plane of the panel. |
| Core plywood | Plywood having a core. |
| Blockboard | Core plywood, the core of which is made of strips of solid wood more than 7 mm wide but not wider than 30 mm, which may or may not be glued together. |
| Laminboard | Core plywood, the core of which is made of strips of rotary cut veneer, not thicker than 7 mm, placed on edge, all or most of which are glued together. |
| Composite plywood | Plywood, the core (or certain layers) of which is made of materials other then solid wood or veneers. There are at least two crossbanded layers on each side of the core. |
| Moulded plywood | Plywood which is not flat, made by pressing in a mould. |
| Long grain plywood | Plywood in which the grain of the outermost plies is parallel or nearly parallel to the long edge of the panel. |
| Cross grained plywood | Plywood in which the grain of the outermost plies is parallel or nearly parallel to the short edge of the panel. |
| Layer | Either one ply or two or more plies glued together with their grain direction parallel or another material. |
| Cross band | Inner layer with grain direction at right angles to the outermost plies. |
| Core | Central layer visible on the edges of the manufactured panel, generally thicker than the other layers and consisting of: - blocks or strips of wood placed side by side which are or are not be glued together; - other wood-based material; - other sheet material; - cellular construction. |
| Veneer | Thin sheet of wood not more than 7 mm in thickness. |
| Sliced veneer | Veneer produced by slicing. |
| Rotary cut veneer | Veneer produced by peeling. |
| Ply | Either one single veneer or two or more veneers joined edge to edge or end to end. |
| Surface | Visible part of outermost ply of a plywood. |
| Face | The better quality surface of a plywood. |
| Back | The opposite surface to the face. |
| Length of a panel | The panel dimension in the direction of the grain of the outermost layers. |
| Width of a panel | The panel dimension at right angle to the length. |
| Thickness of a panel | Dimension perpendicular to the surface of the panel. |
| Grain | General direction or arrangement of fibres. |
| Angle grain | Grain forming an oblique angle with the edges of a ply. |
| Spiral grain | Grain that follows a spiral course around the pith. |
| Interlocked grain | A characteristic of a wood where the fibres in succeeding growth periods incline alternately in opposite directions. |
| Veining | Network formed by veins of wood on the surface of veneer. |
| Curly grain | Grain that follows thight irregular curves. |
| Knot | Portion of a branch embedded in the wood. |
| Intergrown knot | Knot which is intergrown for at least 3 of its perimeter with the surrounding veneer. |
| Partially intergrown knot | Knot which is intergrown for 1 to 3 of its perimeter with the surrounding veneer. |
| Non adhering knot | Knot which is intergrown for less then 1 of its perimeter with the surrounding veneer. |
| Knot hole | Void produced by the removal of a knot. |
| Sound knot | Knot showing no indication of rot. |
| Pin knot | Sound intergrown knot of no more than 5 mm diameter. |
| Check | Separation of the fibres which does not extend through the thickness of the veneer. |
| Splint | Separation of the fibres which extend through the thickness of the veneer. |
| Stain | Any variation from the natural colour of wood, which is not associated with a loss of strength. |
| Resin pocket | Lens-shaped cavity in timber containing or that has contained resin. |
| Bark pocket | Bark that is partly or wholly enclosed in the wood. |
| Roughness | Unevenness of the surface due to irregularities of the structure of the wood or due to defective manufacturing. |
| Open joint | Discontinuity between two adjacent elements in a ply. |
| Overlap (joint) | Defect due to overlapping of two adjacent veneers (or two sections of a split veneer) in a ply. |
| Blister | Localised separation caused by area of glue bond failure between plies. |
| Bump | Local area of over-thickness showing in an outermost ply. |
| Hollow | Local depression in an outermost ply. |
| Imprint | Local indentation caused by foreign matter being pressed into a surface. |
| Inclusion | Foreign matter embedded in a veneer. |
| Plywood sanded only on one side | Plywood the face or back of which has been smoothed by means of a mechanical sander. |
| Plywood sanded on both sides | Plywood the face and back of which has been smoothed by means of a mechanical sander. |
| Scraped plywood | Plywood the face and/or back of which has been smoothed by means of a mechanical scraper. |
| Overlaid plywood | Plywood surfaced with one or several overlay sheets or one or several films such as: - impregnated paper; - plastic; - resin film; - metal; - decorative veneer. |
| Textured plywood | Plywood modified by mechanical method to create greater surface relief. |
| Veneered plywood | Plywood which is overlaid by a decorative wood veneer. |
| Sanding through | Local absence of the outer ply resulting from excessive sanding which reveals some of the glue line (and/or the underlying ply). |
| Glue penetration | Glue which has seeped through the outer ply and which can show up as blemishes. |
| Inserting | Repairing of a ply by an element of determinated shaped sound veneer, inserted to replace defective portions which have been previously removed. |
| Patch (or plug) | Piece of determined shaped veneer for inserting. |
| Shim | Piece of long and narrow shaped veneer for inserting. |
| Filling | Repairing by sealing of open defects with filler. |
| Bond | Adhesion by means of glue. |
| Lay-up | Arrangement of layers in a plywood. |
| Composition | Description of constituent elements of plywood. |
| Cup | Curvature of a panel across the width. |
| Bow | Curvature of a panel across the length. |
| Twist | Spiral distorsion of a panel |